Edge Server
The rapid development of IoT technologies has significantly fueled the growth of cloud storage and big data analytics. With the surge of AI technologies, combined with IoT, the new-generation AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) or Edge AI applications have emerged. These applications demand devices capable of faster responses to manage the vast amounts of data they generate. Cloud computing alone is insufficient to meet the enormous processing power required by AIoT applications. Thus, Edge Computing has become essential, offloading computing tasks from the cloud. With features like low-latency transmission, data load sharing, reduced transmission costs, lower cloud load, real-time computing, and local autonomy, Edge Computing is poised to drive the widespread adoption of AIoT applications.
Edge servers, a key component of Edge Computing infrastructure, are deployed closer to the data source to enable faster processing, quicker responses, and lower latency. These servers provide computing power at the "edge" of the network, facilitating real-time data processing, local storage, and data transfer. Edge servers are especially critical in environments requiring immediate responses, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, video surveillance, and smart city applications. By processing data locally instead of transmitting it to centralized clouds, edge servers not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce reliance on remote data centers.
Edge servers prioritize High-Performance Computing (HPC) to handle complex or large-scale computations at high speeds, boosting the processing capabilities of applications. HPC solutions for edge servers often utilize cluster-computing architectures, connecting multiple nodes with CPUs or GPUs to perform parallel computing. Another popular solution is Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI), which converges servers, storage, networks, and hardware with virtualization software into a single chassis. HCI can expand its performance and capacity by adding nodes to clusters based on computing and storage needs.
Edge servers are pivotal in 5G applications, often termed MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing) servers. As a 5G network architecture, MEC shifts cloud computing and IT services to the network's edge, enabling direct access to data and computing resources via cellular towers. This approach reduces core network loads, ensures low-latency and high-reliability services, and supports essential user equipment (UE) functions like authentication, mobility, and roaming. By incorporating micro data center capabilities with substantial storage capacity, MEC servers localize data and applications, minimizing latency and reducing bandwidth demands.
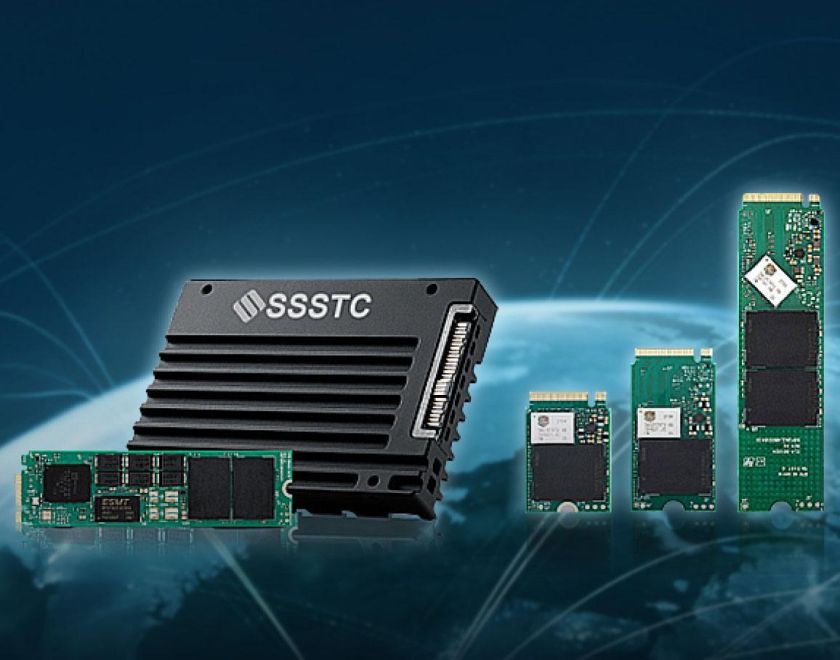
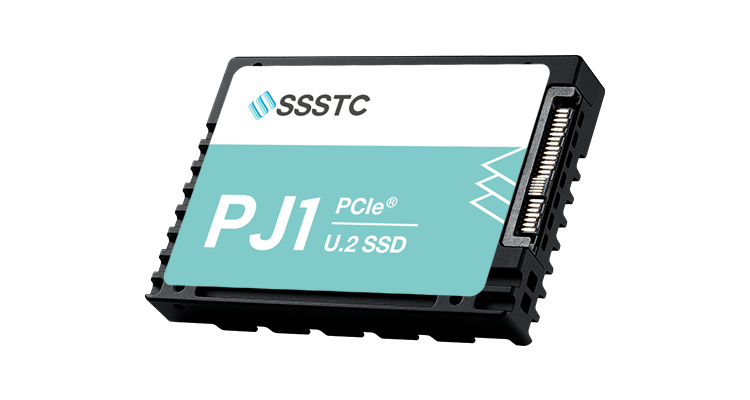
SSDs from Solid State Storage Technology Corporation (SSSTC) are instrumental in realizing low-latency for edge servers, delivering enhanced performance for real-time applications. With superior read and write speeds over traditional HDDs, they efficiently handle large data loads. Equipped with advanced LDPC ECC technology, SSSTC SSDs ensure precise error correction during high-speed transmission, improving data accuracy and access reliability, making them ideal for critical edge computing needs.

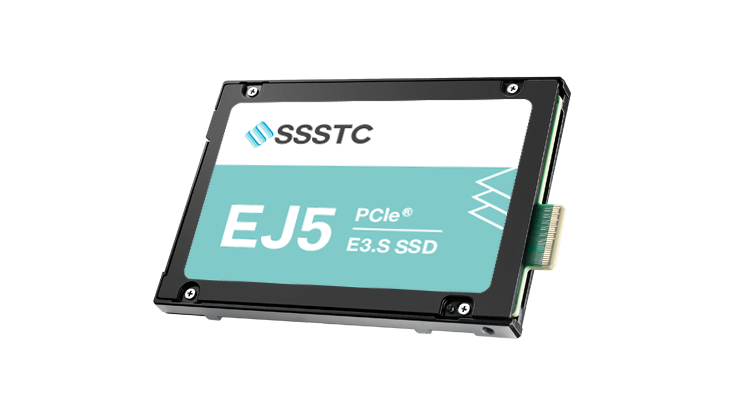
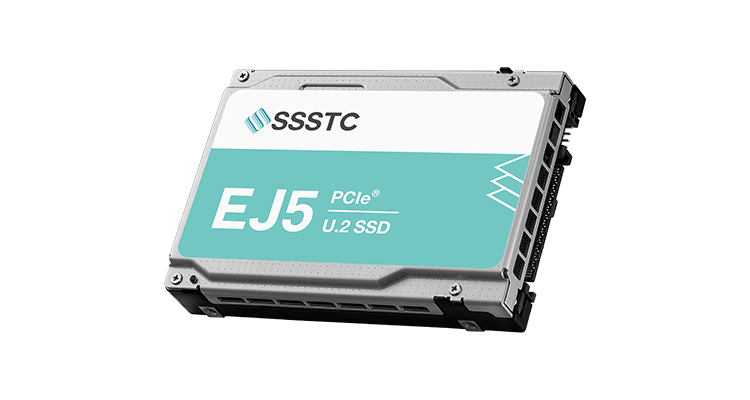
EJ5 series SSD, equipped with TrueLog 360 and TruePLP technology, is the top choice for AI applications.
SSSTC provides the best quality, competitive cost mainstream storage products with superior customized service,using KIOXIA top-quality, reputable NAND flash memory in all our SSD products.Contact us to find more enterprise SSD or industrial SSD solutions.
NVMe™ SSD
960GB / 1920GB / 3840GB / 7680GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6600 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 3500 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
3200GB / 3840GB / 6400GB / 7680GB / 12800GB / 15360GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen5 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 14,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 7,500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
3200GB / 3840GB / 6400GB / 7680GB / 12800GB / 15360GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen5 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 14000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 7500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
1920GB / 3840GB / 7680GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 7,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 4,200 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
960GB / 1920GB / 3840GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,400 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,400 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
3840GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 450 MB/s
















__24C15hqqtC.png)
__24C15wOdCC.png)









__24C05XQ2my.jpg)







__24C05fplcZ.png)
__24C05vgHYC.png)



