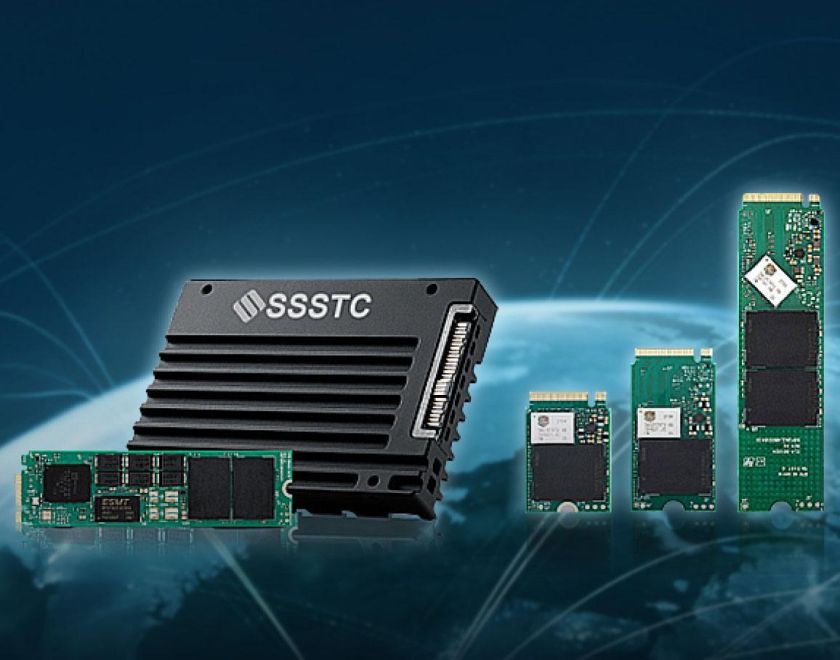
Router
A Router is a networking device that connects two or more networks or network segments. It forwards data packets between different networks or network segments to facilitate data exchange in forming an even more extensive network. As the Routers are the primary node equipment in the internet, and data-forwarding can be determined by routing mechanism. The “Routing” refers to the path undertaken by the data packets being transferred from the “Source Addresses” to the “Destination Addresses”. Each Router along the path only determines the next Router the received packet should be relayed to, and after a series of relays, the packets shall find their way to the destinations.
As the Router can be used to connect at least two networks, the Routers located at the boundary of a LAN connecting with other networks (including the LAN, WAN, or public internet) are called Edge Router. The Routers sitting at the center of the network and transferring data amongst other Routers along the main fiber optic backbone are called Core Routers. Core Routers accommodate higher throughput, often used by telecommunication, internet service providers (ISPs), cloud service providers, or the network of large-scale enterprises with employees spread across multiple buildings or locations. There is a particular One-Armed Router that routes traffic between virtual local area networks (VLANs) on the same physical network segment.
As Routers are commonplace equipment in network management broadly used in all industries, there is a portfolio of products with different functions and specifications. Compared with home-use Routers, enterprise-grade Routers support complex network structures, load-balance, and optimal path routing while carrying multiple users with high speed forwarding and large volume carriage, as well as offering a more robust wireless signal penetration.
The current Routers are not merely transferring data and connecting networks but connect printers, hard disks, VoIP devices, IP cameras, etc. Firewall and content filtering softwares can be embedded into a Router to ensure network security. Much like the Switches, Routers also offer products complemented by PoE (Power Over Ethernet) function to provide power supply to external devices such as VoIP devices, WAP devices, and video surveillance equipment. In the case of the Wireless Router with PoE, it does not just provide power but simplify linework as it offers more flexibility.
Router Working Flow Chart
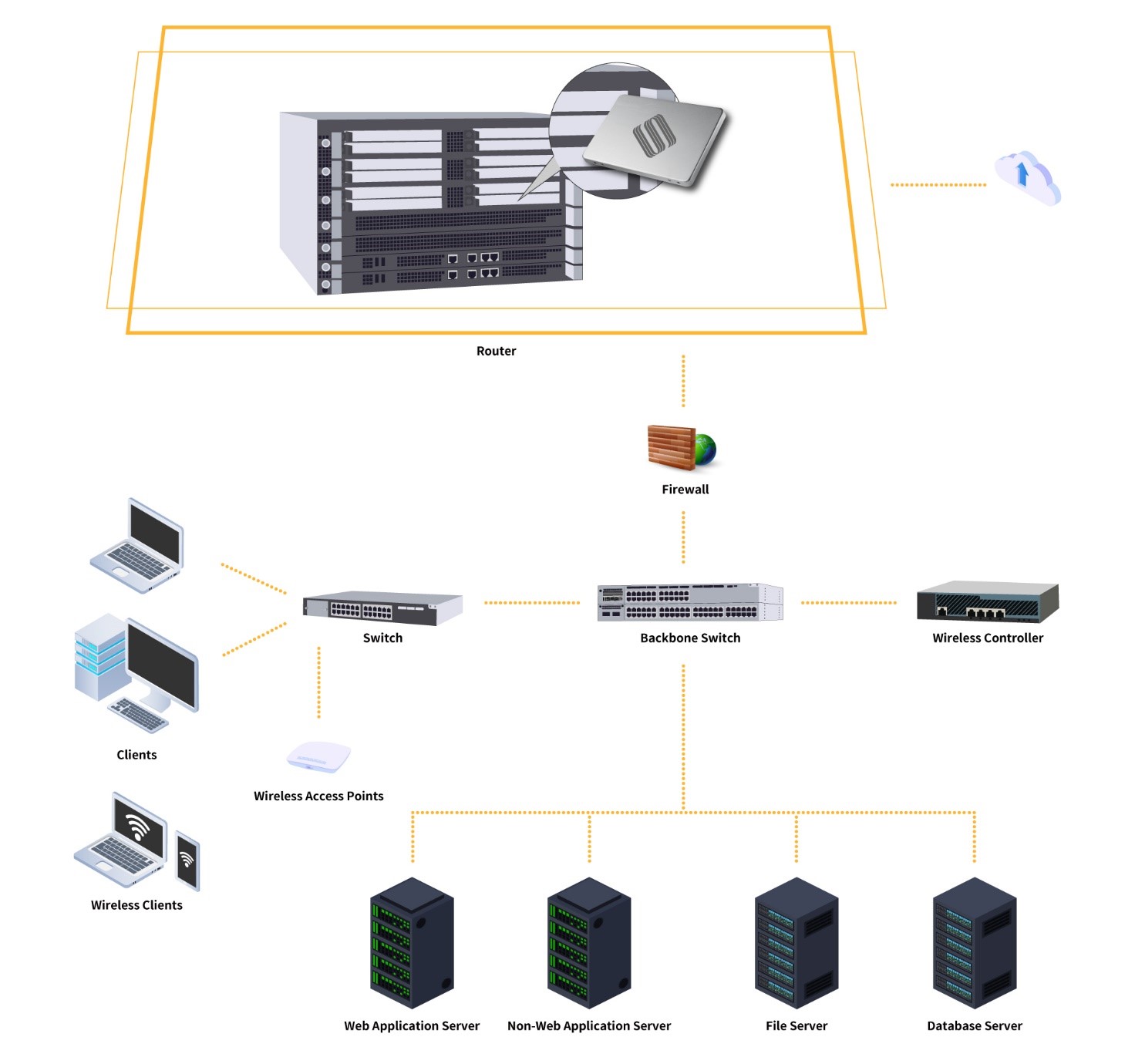
The Routers designed for small and medium-sized enterprises with the built-in M.2 SSD slot are very popular these days, and the mainstream storage capacity is at least 1TB. Once fitted with SSDs, this enables the Routers to serve as micro-servers, much like the mini NAS allowing the convenient file sharing within enterprises, or as the simplified FTP servers to exchange files with external parties. The Routers used by medium and large-sized enterprises usually feature larger storage capacity and forwarding performance, even adopting a routing matrix comprised of multiple Routers in collaboration as a data exchange matrix system, that are identified externally as a single logical Router. This has transcended the limitations of single equipment in terms of capacity, power, cooling, etc., as well as optimizing management convenience.
The enterprise-grade Routers should feature SSDs of enterprise-grade write-intensive products with excellent DWPD and TBW. The reliability of the enterprise-grade PCIe® NVMeTM SSDs and SATA SSDs produced by Solid State Storage Technology Corporation has been tested, according to JEDEC Workload Standard, to design the SSD products that can meet the practical application needs.
Successful Case
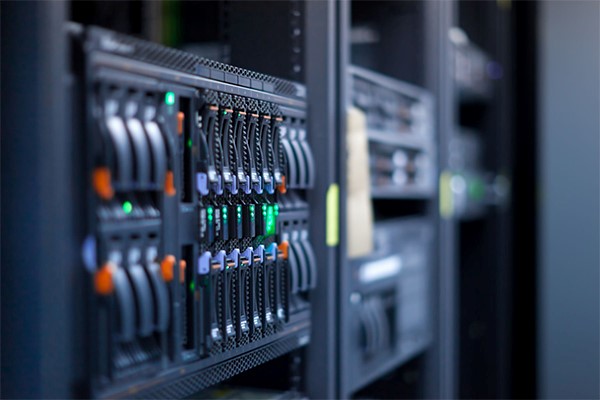

A Taiwan’s renowned ODM manufacturer has introduced SSDs produced by Solid State Storage Technology Corporation to its operations for many years, and many of its Router products, designed for US network equipment providers, feature large-capacity SATA or PCIe® NVMeTM M.2 SSDs of Solid State Storage Technology Corporation.
SSD Model: CVB / CL1 / CA5 Series SSD
NVMe™ SSD
960GB / 1920GB / 3840GB / 7680GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6600 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 3500 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
40GB / 80GB / 128GB / 160GB / 256GB / 320GB / 640GB
NAND Flash: 3D pSLC(TLC)
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: Up to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: Up to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
40GB / 80GB / 160GB / 320GB / 640GB
NAND Flash: 3D pSLC(TLC)
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: Up to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: Up to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
40GB / 80GB / 160GB / 256GB / 320GB / 640GB
NAND Flash: 3D pSLC(TLC)
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
120GB / 128GB / 256GB / 480GB / 512GB / 960GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
80GB / 160GB / 320GB
NAND Flash: 3D pSLC(TLC)
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 3700 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2600 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
40GB / 80GB / 160GB / 320GB / 640GB /1280GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: 3,100 MB/s
Sequential Write: 1,500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
40GB / 80GB / 160GB / 320GB / 640GB /1280GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: 3,100 MB/s
Sequential Write: 1,500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
1920GB / 3840GB / 7680GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 7,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 4,200 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
80GB / 160GB / 320GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 3,500 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,100 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB /4096GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: 3,100 MB/s
Sequential Write: 1,500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB /4096GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: 3,100 MB/s
Sequential Write: 1,500 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,800 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 4,800 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
240GB / 256GB /480GB/ 512GB / 960GB/ 1024GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 3,700 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,600 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
256GB / 512GB / 1024GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 3,700 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,600 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 2,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 1,100 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB/ 1024GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 2,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 1,100 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 3,700 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,600 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 5,300 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 5,300 MB/s
SATA SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 450 MB/s
SATA SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 450 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
960GB / 1920GB / 3840GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,400 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 2,400 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen3 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 2,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 1,100 MB/s
NVMe™ SSD
256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: 5,300 MB/s
SATA
128GB / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
3840GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 520 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 520 MB/s
SATA SSD
240GB / 480GB / 960GB / 1920GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 450 MB/s
SATA SSD
128GB / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
SATA SSD
128G / 256GB / 512GB / 1024GB / 2048GB
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s






































__24C15hqqtC.png)
__24C15wOdCC.png)









__24C05XQ2my.jpg)







__24C05fplcZ.png)
__24C05vgHYC.png)



