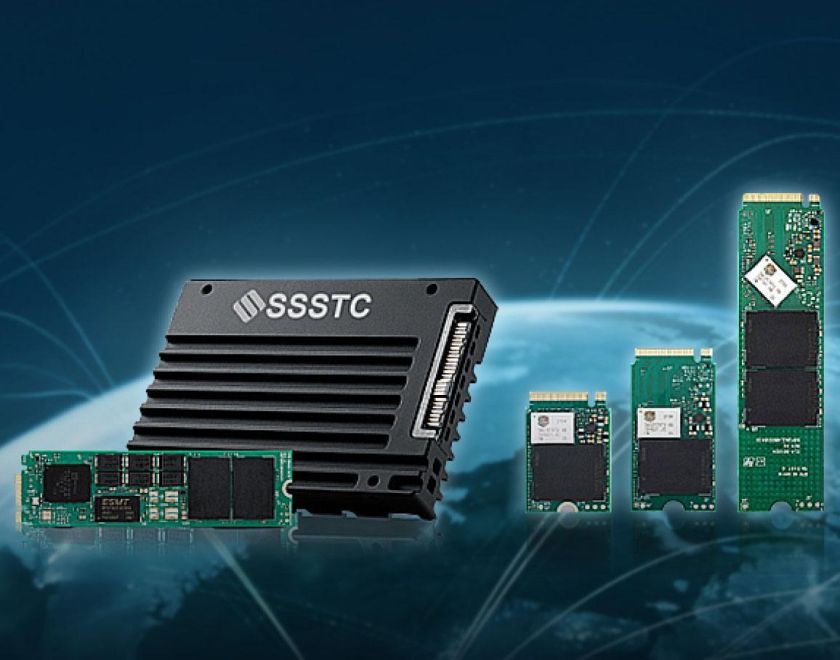
Comprehensive Guide to SSD Form Factors: 2.5", mSATA, M.2, & U.2 Explained
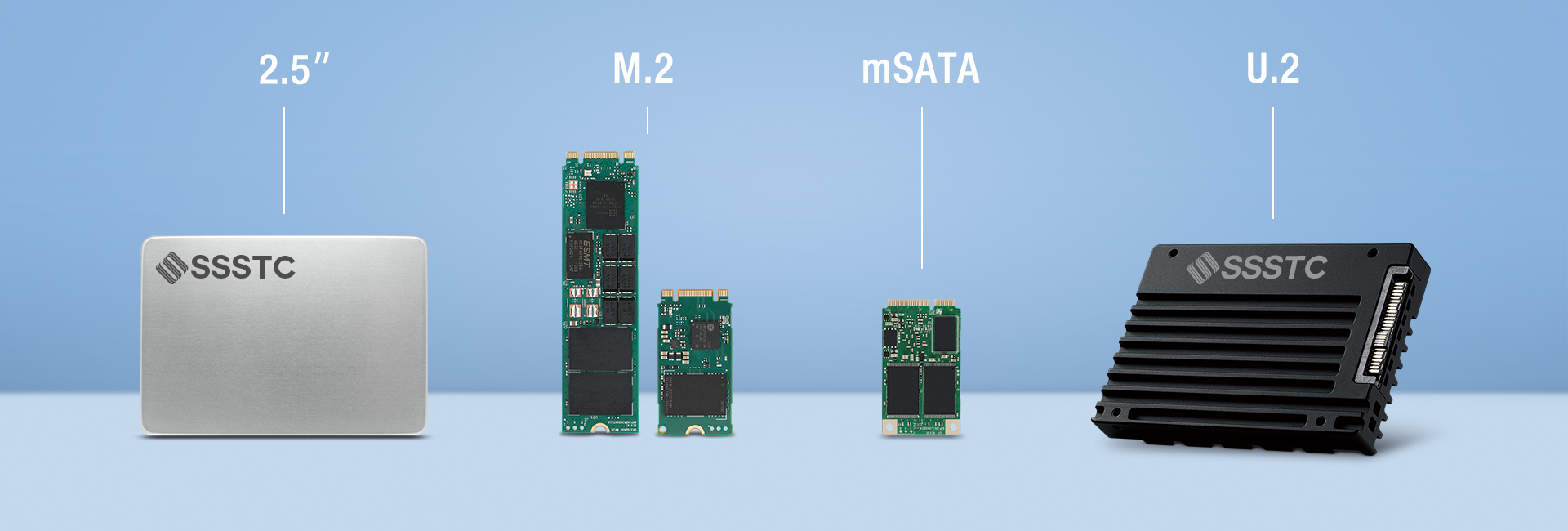
The different SSD form factors: 2.5", mSATA, M.2, U.2
Solid-state drives (SSDs) have become an integral part of modern computing, offering faster speeds and improved reliability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs come in various form factors, each designed to fit specific applications and requirements. In this article, we will explore and compare four popular SSD form factors: 2.5", mSATA, M.2, and U.2. Understanding the differences between these form factors will help you make an informed decision when choosing the right SSD for your needs.
l 2.5" Form Factor:
The 2.5" form factor is a standard size used for both SSDs and HDDs. With dimensions of 2.75" x 3.95", it is widely compatible with most laptops and desktops. 2.5" SSDs are typically connected via a SATA interface, offering good performance and ease of installation. However, they may not offer the same level of speed and compactness as other form factors discussed below.
An excellent example of this is the CVB SATA SSD, a 2.5" SSD utilizing the SATA interface. It strikes a perfect balance between performance and cost. The specific design of the CVB SATA SSD makes it an ideal choice for many users, as it can be easily adapted to fit most laptops and desktop computers.

CVC 2.5''
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: SATA 3 (6Gb/s)
Sequential Read: UP to 550 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 510 MB/s
l mSATA Form Factor:
mSATA, short for mini-SATA, is a smaller form factor primarily designed for ultrabooks and tablets. Measuring 1.18" x 2", it is an ideal solution for devices with limited space. mSATA SSDs are connected via a Mini PCI Express (PCIe) slot and provide decent performance.
As an example, the U8 mSATA SSD is a specific model within the mSATA interface that represents an advanced application of this technology. It aligns with the standard dimensions and performance needs of mSATA. However, the mSATA form factor has become less common in recent years, as it has been largely replaced by the more compact and versatile M.2 form factor.
Nevertheless, U8 mSATA SSD and other mSATA products still hold their unique purposes and value. They may be the more suitable choice in certain applications, especially in space-constrained environments or where specific performance criteria are needed.
l U.2 Form Factor:
U.2, formerly known as SFF-8639, is a form factor designed specifically for enterprise-grade SSDs. These U.2 SSDs resemble 2.5" drives in size but use a different connector and interface. They utilize the PCIe interface and provide faster speeds compared to SATA-based SSDs.
An example of the utilization of this form factor is the LJ1 (U.2) SSD. As a specific model within the U.2 family, LJ1 (U.2) represents the high-performance standards required in data centers and server environments. Its particular design and features align with the specific needs of enterprise applications.
U.2 SSDs, including models like LJ1 (U.2), are commonly found in data centers and server environments that require high-performance storage solutions. Their robust design and high-speed capabilities make them a preferred choice in many professional settings.

EJ5 Series:Designed for AI, Machine Learning (ML), virtualization, and real-time data analytics.
Mixed-use (3 DWPD for 5 years): 3200GB / 6400GB / 12800GB
l M.2 Form Factor:
The M.2 form factor has gained significant popularity due to its small size and high performance. M.2 SSDs are rectangular in shape and usually range in length from 22mm to 80mm. They are connected directly to the motherboard via the M.2 slot, thus eliminating the need for cables and reducing clutter within the system. M.2 SSDs can utilize either the SATA or PCIe interface, with the latter offering faster speeds.
As an example, the CL4 Series PCIe® M.2 2280 SSD is one of the high-performance M.2 SSDs that uses the PCIe interface, offering extremely high read and write speeds, and is especially suitable for those who need fast storage solutions.
CL6 M.2 2280
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: 5,300 MB/s
When it comes to SSD form factors, the choice depends on your specific requirements and the device in which the SSD will be installed. The 2.5" form factor offers compatibility and ease of installation, while mSATA suits smaller devices with limited space. The M.2 form factor strikes a balance between size, performance, and compatibility, making it a popular choice for many users. On the other hand, the U.2 form factor is more specialized, primarily catering to enterprise-grade storage needs.
Understanding the differences and advantages of each SSD form factor will help you select the right SSD for your system. Consider factors such as device compatibility, available slots, and desired performance to make an informed decision. By choosing the appropriate SSD form factor, you can optimize your system's storage capabilities and improve overall performance.
SSSTC provides the best quality, competitive cost mainstream storage products with superior customized service.Contact us to find more enterprise SSDs or industrial SSDs solutions.
-
SSSTC SATA SSD
Widely used in rugged computers, laptops, servers, edge servers, video surveillance systems, and enterprise-level storage solutions, they offer stable and dependable data storage. -
SSSTC NVMe™ SSD
With high-speed transfer and low latency, it's used in data centers, cloud services, big data, gaming, and graphics, enhancing system performance and speed.


__24C05D67dI.webp)

__24C15hqqtC.png)
__24C15wOdCC.png)









__24C05XQ2my.jpg)






__24C05fplcZ.png)
__24C05vgHYC.png)



